A Complete Guide to Vertical Spreads in Options Trading
Vertical spreads are one of the most versatile strategies available to options traders. Instead of simply buying or selling a single option, a vertical spread is constructed by simultaneously buying and selling options of the same type (calls or puts) and expiration date, but at different strike prices. Vertical spreads are a powerful tool, but if you're brand-new to options, you may want to review the basics first. Check out our Beginner's Guide to Options Trading before diving deeper.
Why use vertical spreads? They allow traders to:
- Reduce the cost of entry compared to buying a single option outright.
- Define both maximum profit and maximum loss in advance.
- Express bullish or bearish views on a stock with limited risk.
There are four main types of vertical spreads:
Below, we'll break down how each vertical spread works, when to use them, and their risk/reward profiles.
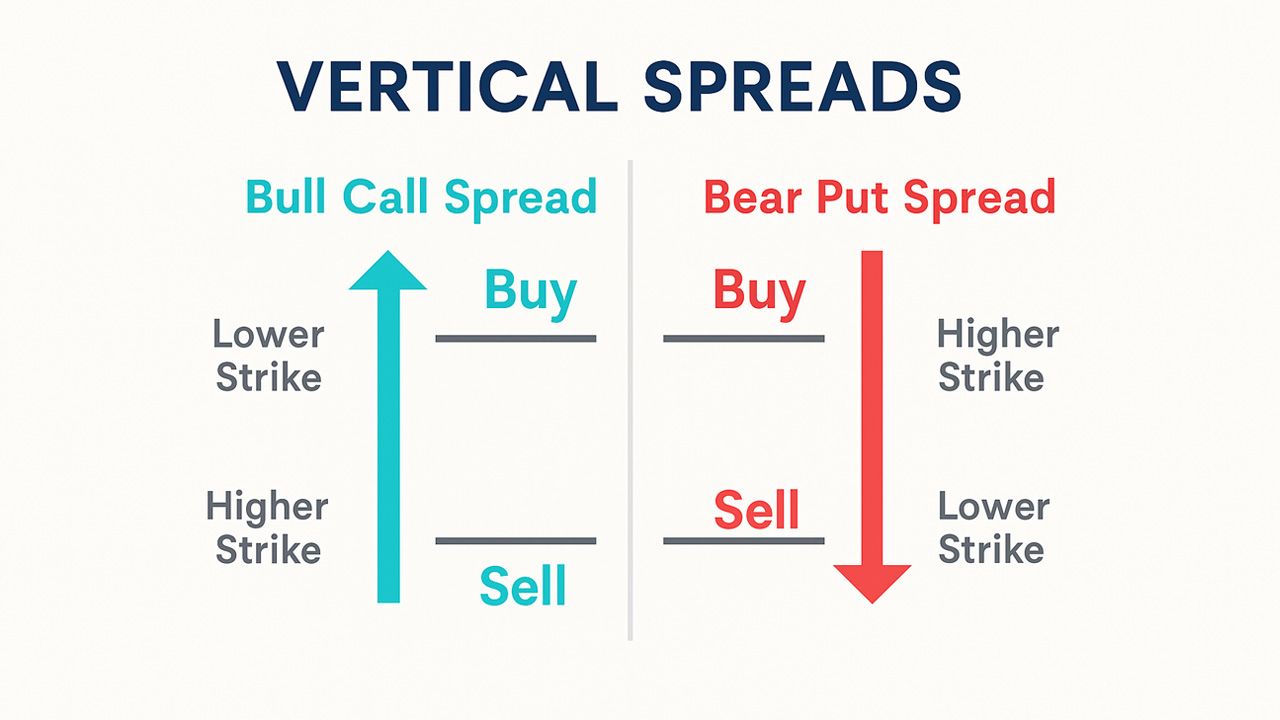
1️⃣ Bull Call Spread
The bull call spread is a bullish vertical spread that profits from a moderate rise in a stock's price. It's also known as a long call spread or call debit spread.
🔗 How to set up:
- Buy a call option at a lower strike price.
- Sell another call option at a higher strike price.
- Both options have the same expiration date.
🎢 Profit potential:
- Gains occur as the stock rises.
- Maximum profit happens if the stock closes at or above the short call strike at expiration.
⚠️ Breakeven and risk/reward:
- Breakeven = Long call strike + net premium paid.
- Max profit = (Spread width - premium paid) × 100.
- Max loss = Premium paid × 100.
📌 Example:
- Buy the 135 Call for $9.30.
- Sell the 150 Call for $1.54.
- Net cost = $7.76.
- Breakeven = $142.76.
- Max profit = $724.
- Max loss = $776.
Summary:
A bull call spread is a controlled way to profit from moderate stock price increases while capping risk.
2️⃣ Bear Call Spread
The bear call spread is a bearish vertical spread that generates income when the stock price declines or stays flat. Also known as a short call spread or call credit spread.
🔗 How to set up:
- Sell a call option at a lower strike price.
- Buy another call option at a higher strike price.
- Both options have the same expiration.
🎢 Profit potential:
- Gains come from the premium received.
- Maximum profit occurs if the stock stays below the short call strike at expiration.
⚠️ Breakeven and risk/reward:
- Breakeven = Short call strike + net premium received.
- Max profit = Premium received × 100.
- Max loss = (Spread width - premium received) × 100.
📌 Example:
- Sell the 142 Call for $1.93.
- Buy the 145 Call for $0.87.
- Net credit = $1.06.
- Breakeven = $143.06.
- Max profit = $106.
- Max loss = $194.
Summary:
A bear call spread is ideal for traders expecting a stock to trade sideways or move lower, with limited risk exposure.
3️⃣ Bear Put Spread
The bear put spread is a bearish vertical spread designed for traders who expect a moderate decline in stock price. It's also called a long put spread or put debit spread.
🔗 How to set up:
- Buy a put option at a higher strike price.
- Sell another put option at a lower strike price.
- Both options share the same expiration.
🎢 Profit potential:
- Gains occur as the stock falls.
- Maximum profit happens if the stock closes at or below the short put strike.
⚠️ Breakeven and risk/reward:
- Breakeven = Long put strike - premium paid.
- Max profit = (Spread width - premium paid) × 100.
- Max loss = Premium paid × 100.
📌 Example:
- Buy the 800 Put for $44.88.
- Sell the 750 Put for $22.63.
- Net debit = $22.25.
- Breakeven = $777.75.
- Max profit = $2,775.
- Max loss = $2,225.
Summary:
A bear put spread is a cost-effective way to profit from moderate downside moves while keeping losses defined.
4️⃣ Bull Put Spread
The bull put spread is a bullish vertical spread that profits when the stock rises or trades sideways. It's also known as a short put spread or put credit spread.
🔗 How to set up:
- Sell a put option at a higher strike price.
- Buy another put option at a lower strike price.
- Same expiration cycle.
🎢 Profit potential:
- Gains come from the premium received.
- Maximum profit occurs if the stock stays above the short put strike at expiration.
⚠️ Breakeven and risk/reward:
- Breakeven = Short put strike - premium received.
- Max profit = Premium received × 100.
- Max loss = (Spread width - premium received) × 100.
📌 Example:
- Sell the 145 Put for $6.60.
- Buy the 135 Put for $3.07.
- Net credit = $3.53.
- Breakeven = $141.47.
- Max profit = $353.
- Max loss = $647.
Summary:
The bull put spread is a powerful strategy for generating income when expecting the stock to remain stable or trend higher.
Final Thoughts on Vertical Spreads
Vertical spreads are a cornerstone of options trading because they offer:
⚡ Defined risk and reward.
⚡ Flexibility to trade both bullish and bearish views.
⚡ Lower capital requirements compared to single-leg options.
Whether you're trading a bull call spread, bear call spread, bear put spread, or bull put spread, vertical spreads can help you manage risk and structure trades with clear outcomes. Once you're comfortable trading vertical spreads, you can expand your toolkit with more complex positions like iron condors. Learn how in our guide Weekly Iron Condors for Income: A Practical Guide for Traders.
Stay Connected!
Join our mailing list to get notified of all new blog posts, and receive the latest news and updates from our team.

